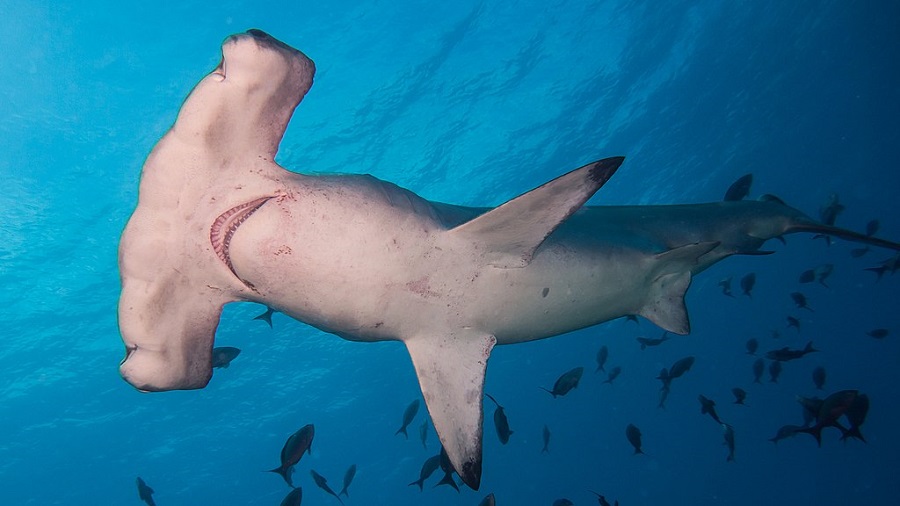
Hammerhead shark. Photo by Kris Mikael Krister, Wikimedia Commons.
Recreational fishers are increasingly targeting sharks and rays, a situation that is causing concern among researchers.
A new study by an international team of scientists reveals that recreational catches of these fishes have gradually increased over the last six decades around the world, now accounting for 5-6 per cent of the total catches taken for leisure or pleasure.