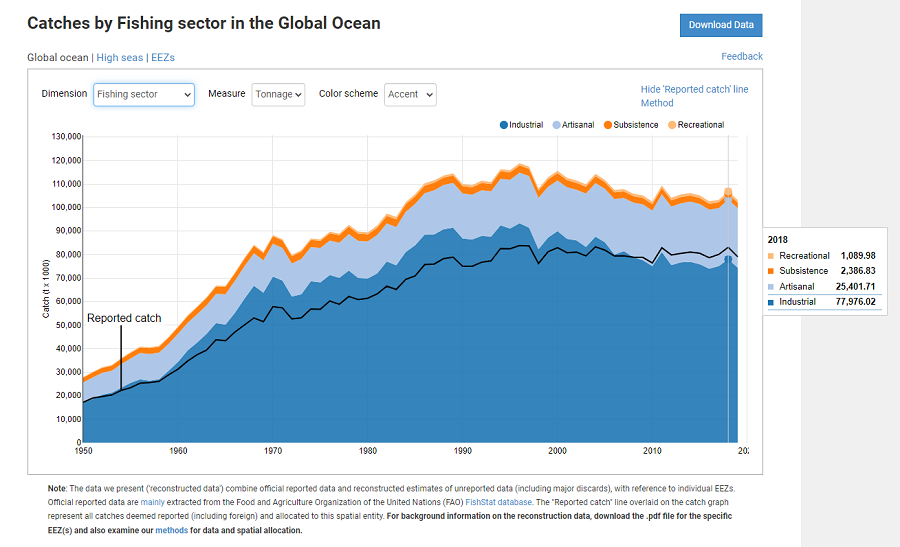
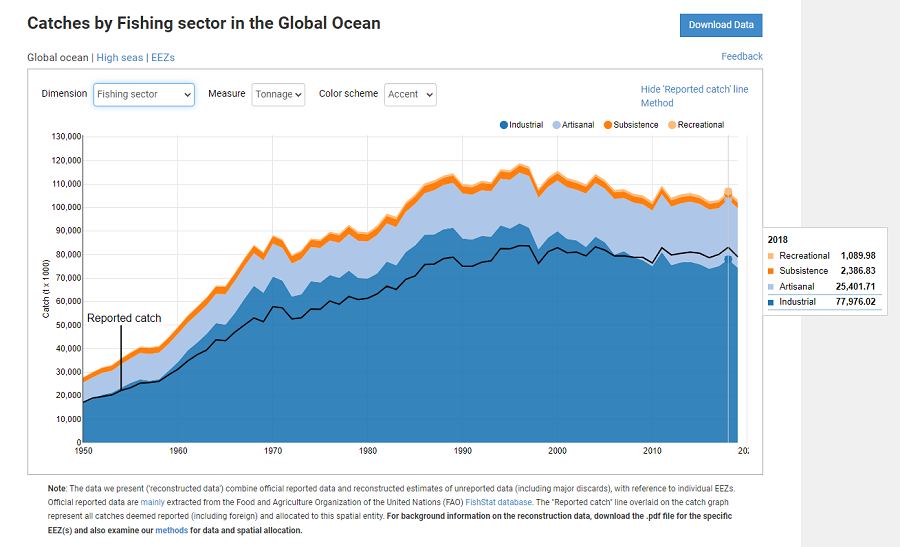
The Sea Around Us is pleased to announce that the marine fisheries catch data and derived indicators have been updated to the year 2018.
Tag: fisheries data
Tilapias are not precocious, they are just resilient

Nile tilapia. Photo by Germano Roberto Schüür, Wikimedia Commons.
Tilapias living in crowded aquaculture ponds or small freshwater reservoirs adapt so well to these stressful environments that they stop growing and reproduce at a smaller size than their stress-free counterparts.
Who supports FishBase and SeaLifeBase?
Maintaining big data projects takes a lot. A lot of people to conduct research, populate databases, verify information, make the data accessible. It also requires a lot of material and financial resources.
World Fisheries Day 2020 – what research has found
November 21st marks World Fisheries Day.
According to the Institute for Fisheries Resources, this day has been celebrated since November 21st, 1997, when the World Fisheries Forum (WFF) was officially established in New Delhi, India. This non-profit organization is now known as the World Forum of Fish Harvesters and Fishworkers.
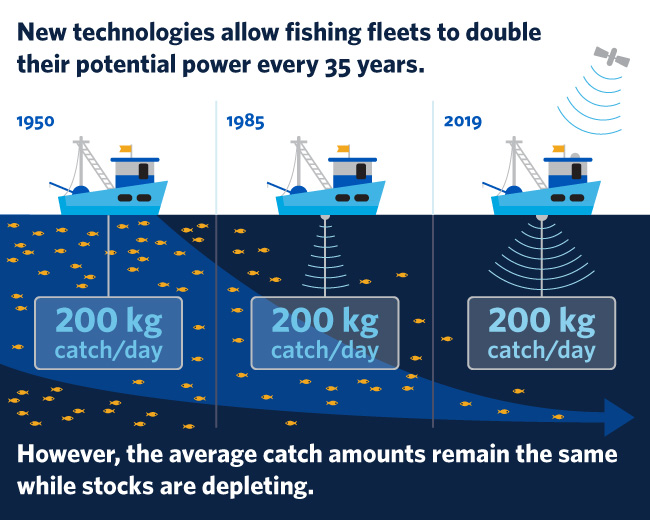
New technology allows fleets to double fishing capacity — and deplete fish stocks faster
Technological advances are allowing commercial fishing fleets to double their fishing power every 35 years and put even more pressure on dwindling fish stocks, new research has found.
Researchers from the Sea Around Us initiative at the University of British Columbia analyzed more than 50 studies related to the increase in vessels’ catching power and found that the introduction of mechanisms such as GPS, fishfinders, echo-sounders or acoustic cameras, has led to an average two per cent yearly increase in boats’ capacity to capture fish.