Photo by WWF.
Humanity and the way we feed, fuel and finance our societies and economies are pushing nature and the services that power and sustain us to the brink, according to WWF’s Living Planet Report 2018. The report, released today, presents a sobering picture of the impact of human activity on the world’s wildlife, forests, oceans, rivers and climate, underlining the rapidly closing window for action and the urgent need for the global community to collectively rethink and redefine how we value, protect and restore nature.
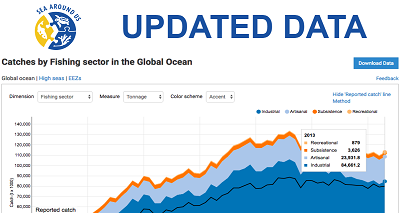
The Living Planet Report 2018 presents a comprehensive overview of the state of our natural world, twenty years after the flagship report was first published. Through indicators such as the Living Planet Index (LPI) provided by the Zoological Society of London, the Species Habitat Index (SHI), the IUCN Red List Index (RLI), the Biodiversity Intactness Index (BII) and the Sea Around Us fisheries data, as well as Planetary Boundaries and the Ecological Footprint, the report paints a singular disturbing picture: human activity is pushing the planet’s natural systems that support life on earth to the edge.
Continue reading →